Armature Reaction
At No Load there is not any current flow in the Armature Winding it means Ia = 0 So MMF=NI =0 that means No Armature Flux will Generate But when the load is applied then Ia is not equal to zero and MMF Produce a flux known as Armature Flux.
Armature Reaction -
The Effect of Armature Flux to the main field flux such that it Magnetised, Demagnetized or Cross Magnetized the Resultant flux.
Type of Armature Reaction -
In D.C. Circuit the load is only Resistive type but for A.C. Circuit the load may be Three Types.
1 - Resistive Load
2 - Inductive Load
3 - Capacitive Load
In Case of Resistive Load -
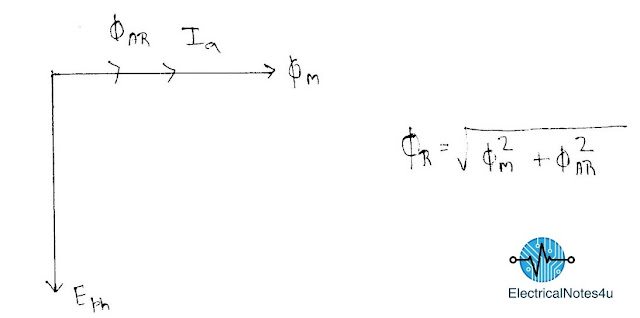
In this case, The Armature flux lag the main flux by an Angle of 90° so the Resultant flux just higher to main field flux That Phenomena is known as Cross Magnetization.
In Case of Inductive Load -
In This case, the Armature Flux Directly Oppose the main field flux by an Angle of 180° due to this effect the Resultant flux decreases and this Phenomena is known as Demagnetization.
In Case of Capacitive Load -
In This Case, Main field flux and Armature Flux are in the same Direction due to Capacitive load the Resultant flux Increases That Phenomena is known as Magnetization.
Tags -
#electrical engineering notes
#Armature Reaction in Electrical Engineering






0 comments:
Post a Comment